Best Things to Do First Thing in the Morning for Weight Loss Results

Hey Angels and Alphas,
Starting your day with the right habits can set a positive tone for the rest of the day and significantly boost your weight loss efforts. Incorporating morning routines that focus on physical activity, nutrition, and mental well-being can help you stay on track with your weight loss goals.
Here are some of the best things to do first thing in the morning for effective weight loss:
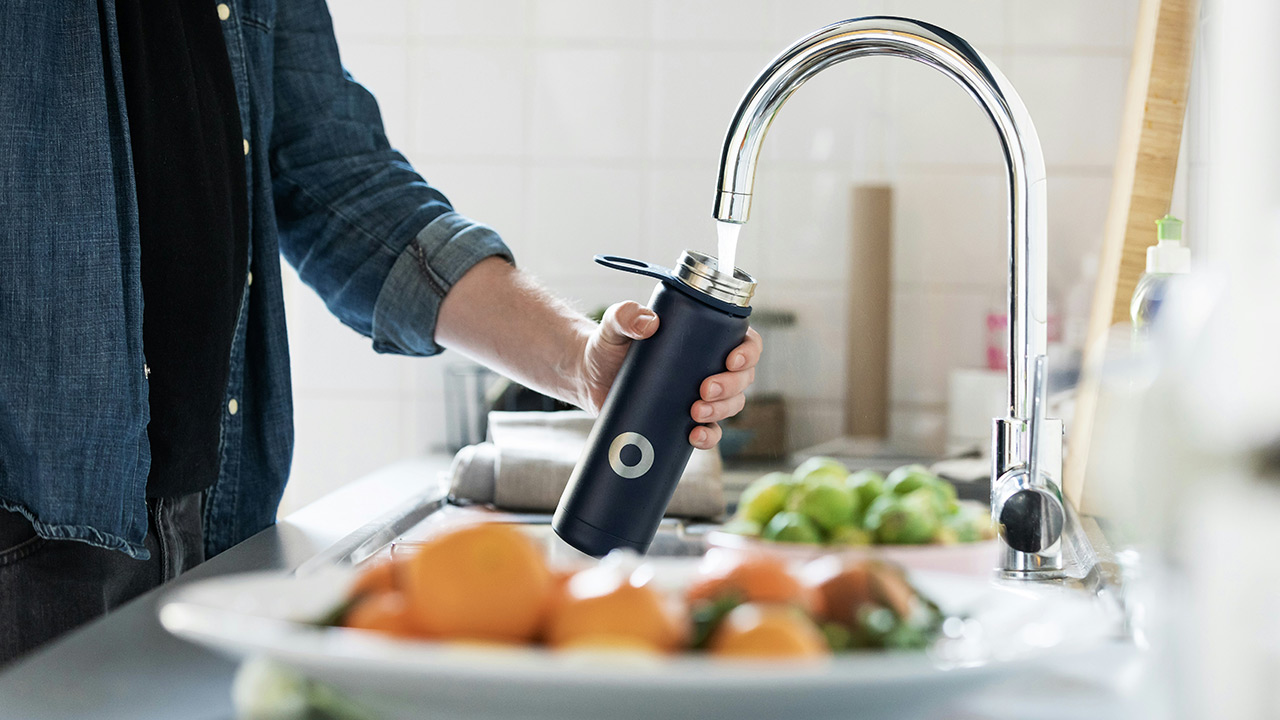
1. Hydrate with Water
Drinking a glass of water as soon as you wake up is crucial. After a night of sleep, your body is naturally dehydrated. Hydrating first thing in the morning kick-starts your metabolism, helps flush out toxins, and prepares your digestive system for the day ahead. Adding a slice of lemon can provide a refreshing flavor and additional health benefits, such as improved digestion and a boost in vitamin C.
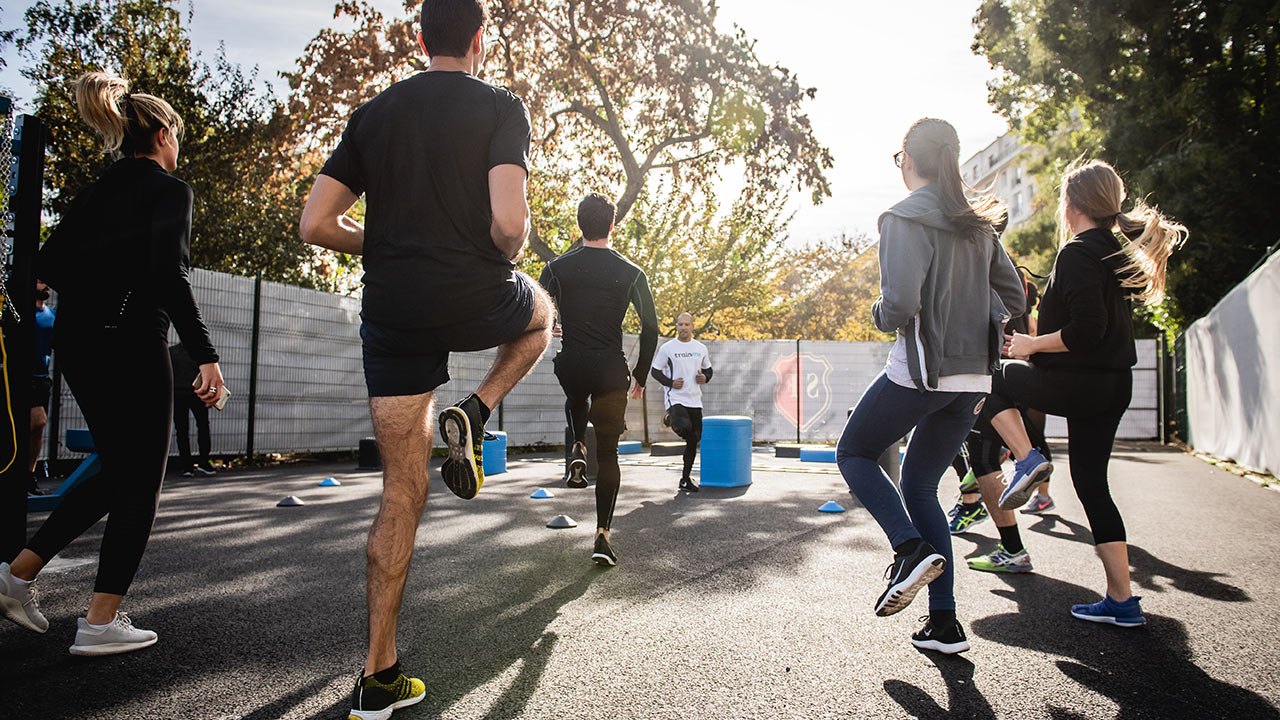
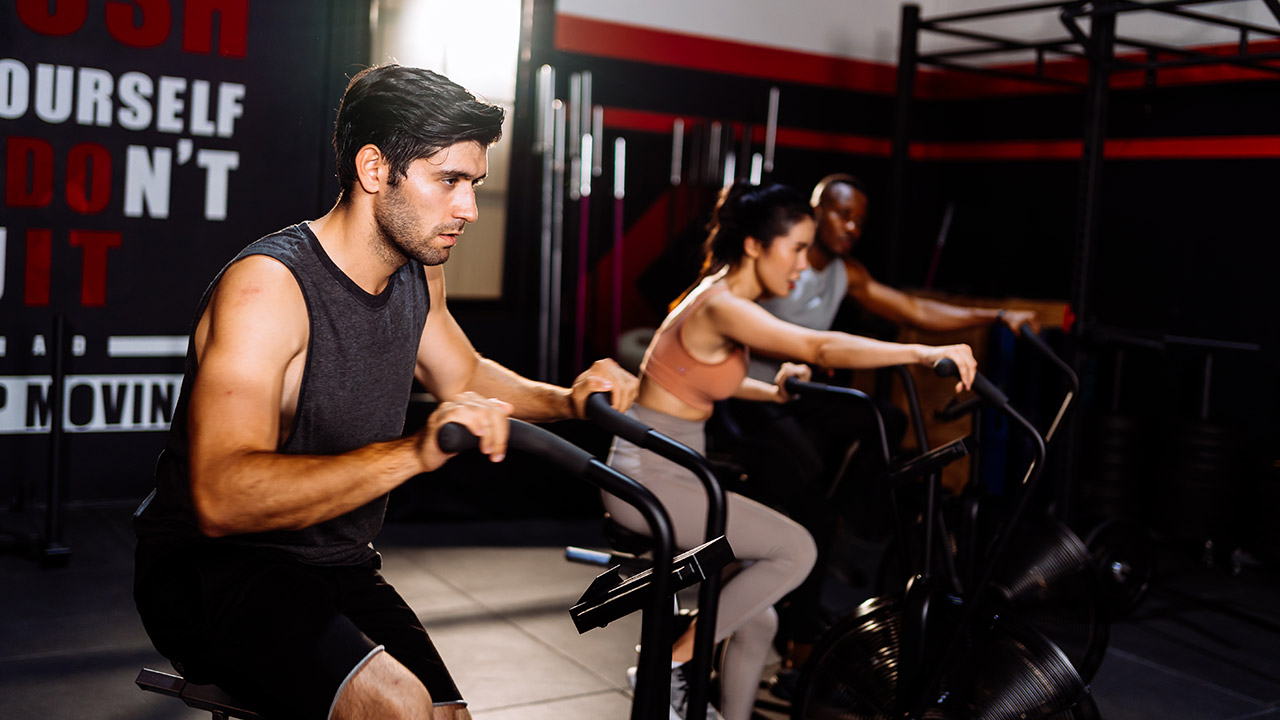
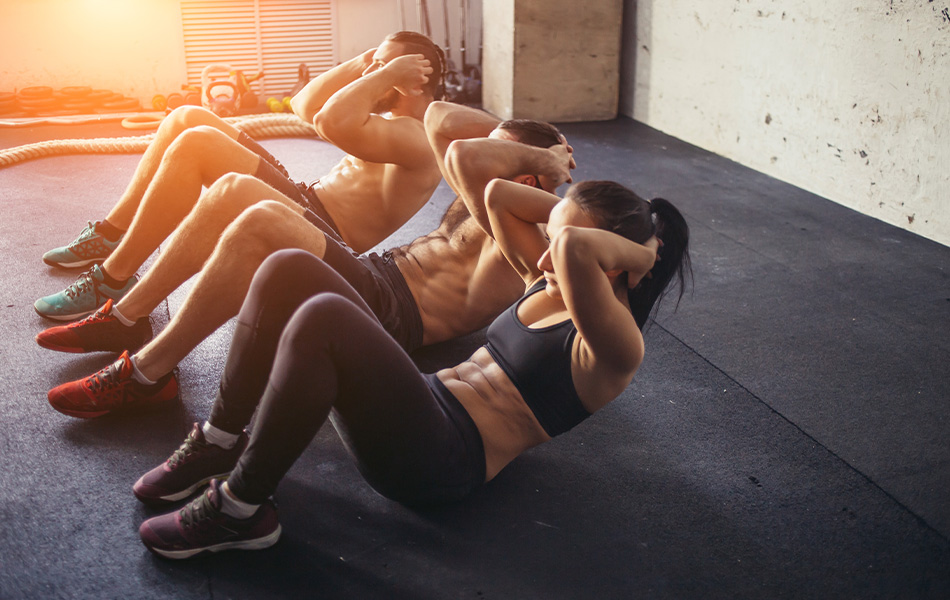
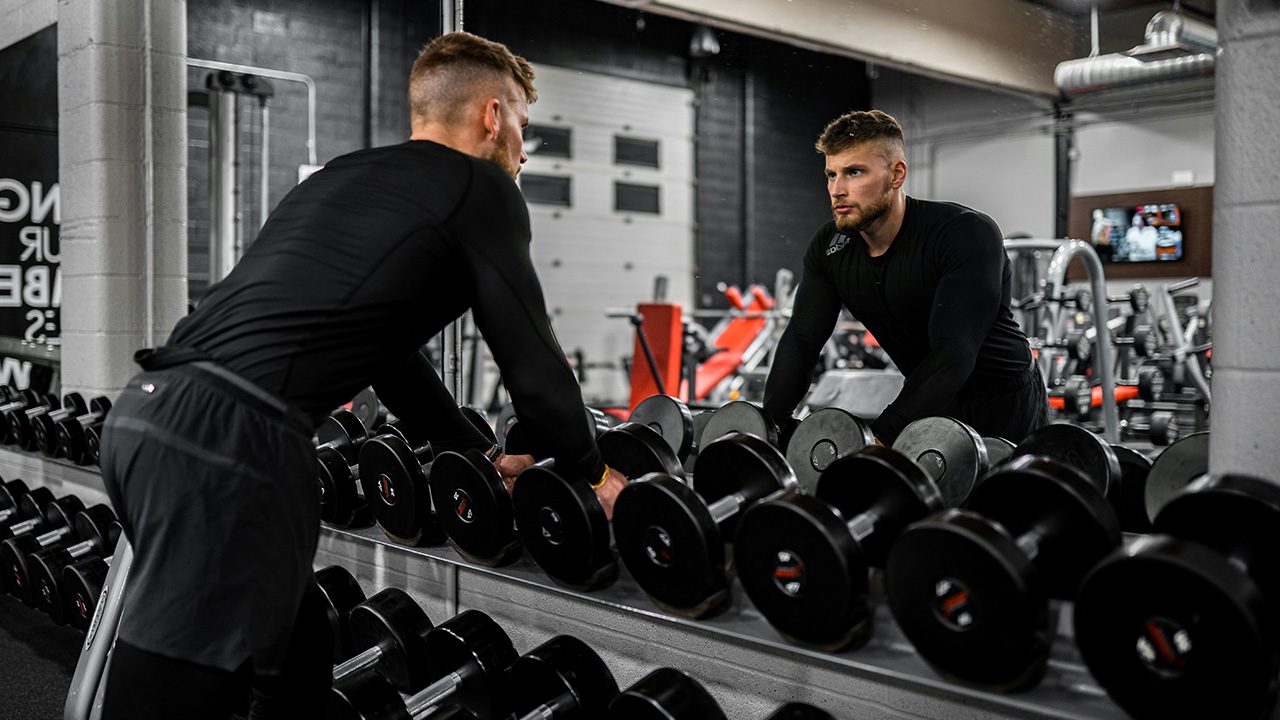
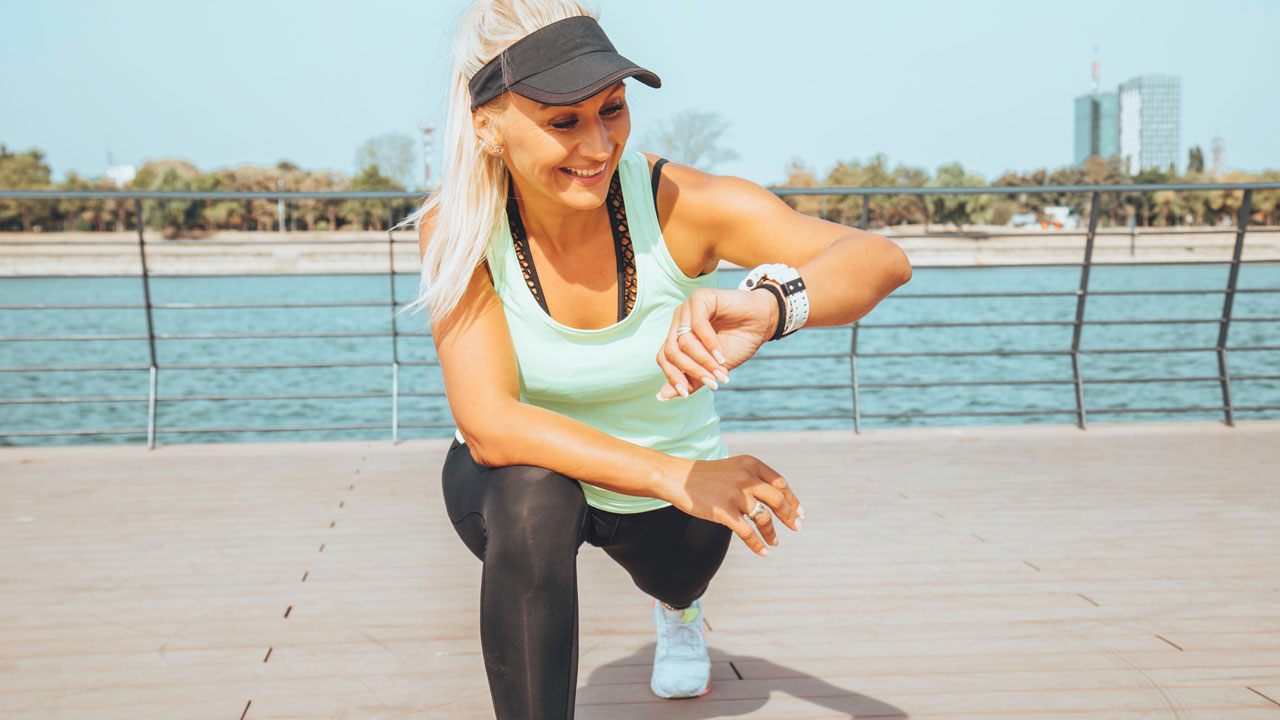
2. Engage in Morning Exercise
Exercising in the morning can be highly effective for weight loss. Morning workouts can help you burn more fat, as your body’s glycogen levels are lower after fasting overnight. This means your body might turn to fat stores for energy. Whether it’s a brisk walk, a jog, a yoga session, or a high-intensity interval training (HIIT) workout, starting your day with physical activity can boost your energy levels, improve your mood, and enhance your overall metabolism.
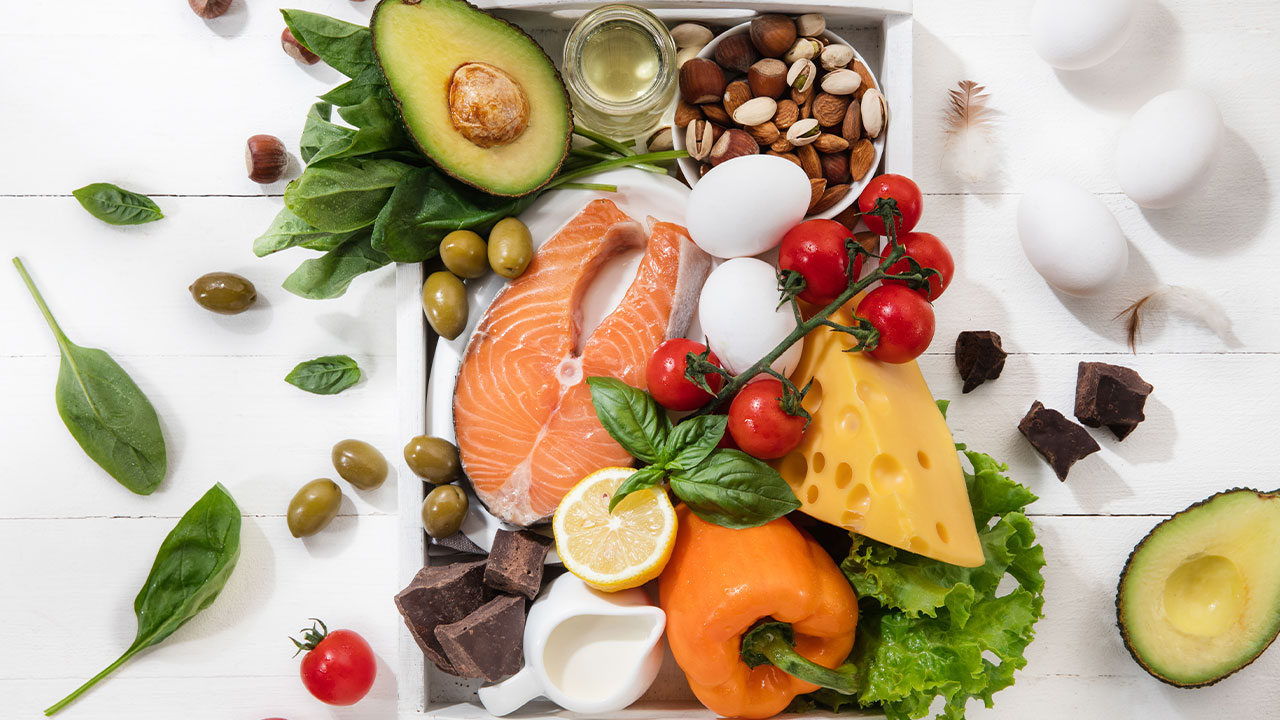
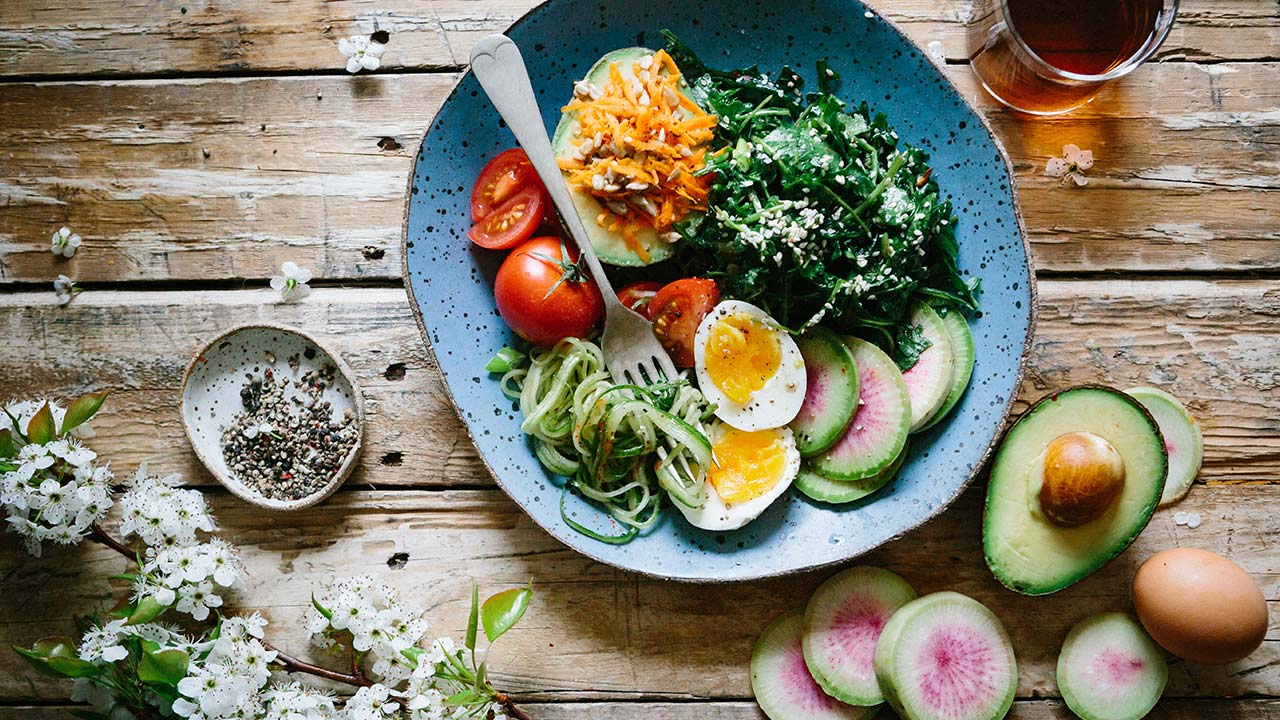
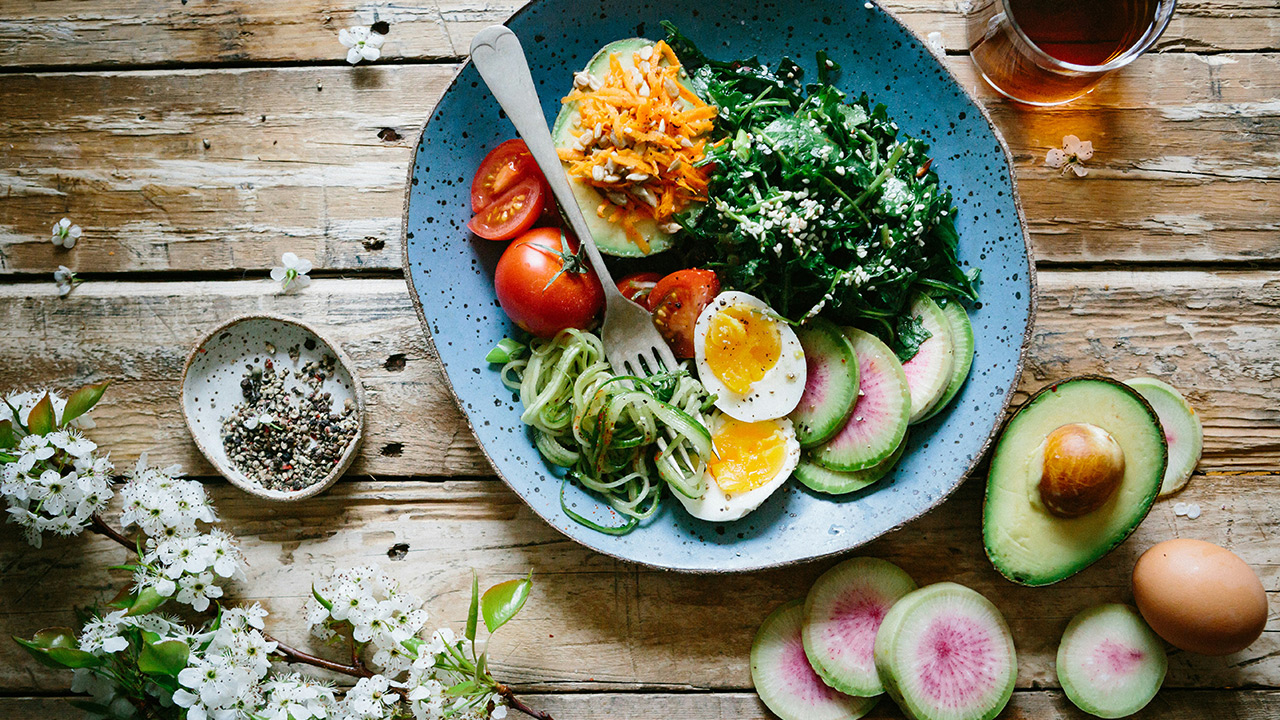
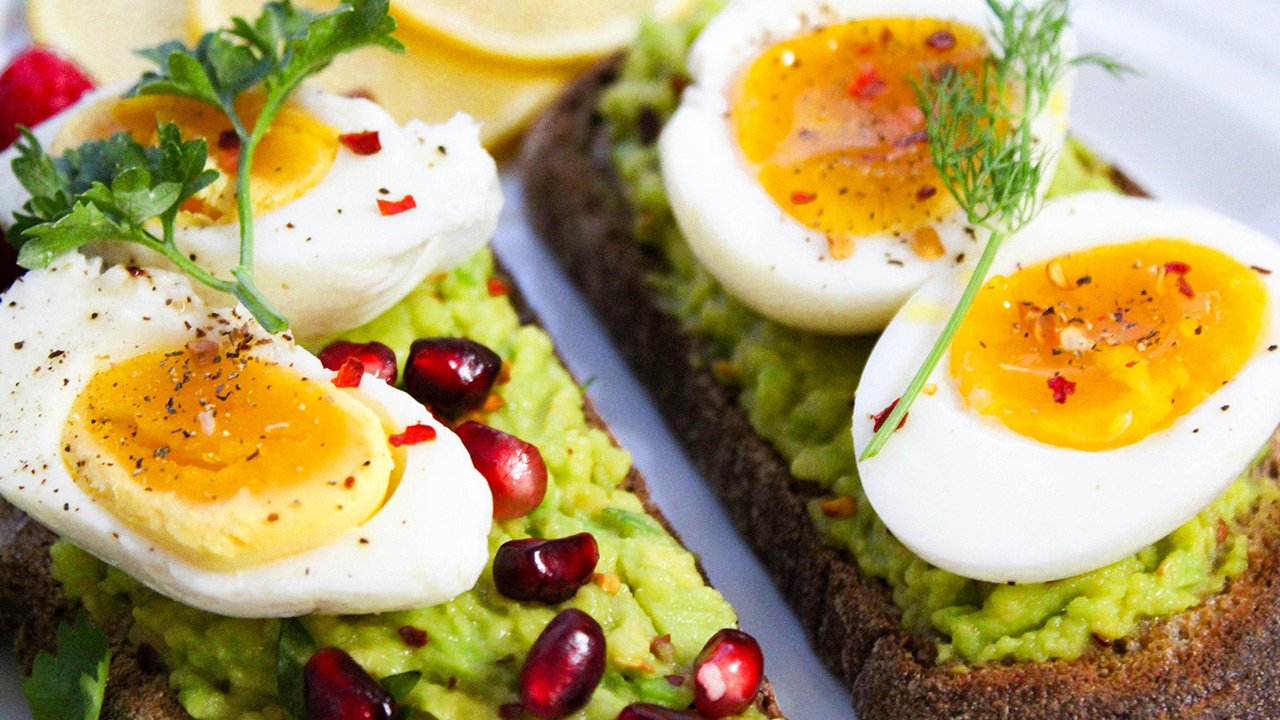
3. Eat a Protein-Rich Breakfast
A protein-rich breakfast can keep you fuller for longer, reducing cravings and preventing overeating later in the day. Include foods such as eggs, Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, or a protein smoothie. Protein helps in maintaining muscle mass while you lose fat, which is essential for a healthy metabolism.
4. Practice Mindfulness or Meditation
Taking a few minutes to practice mindfulness or meditation in the morning can help reduce stress levels and improve mental clarity. High stress can lead to emotional eating and weight gain. Starting your day with a calm mind can help you make better food choices and stay committed to your weight loss goals.
5. Plan Your Meals and Snacks
Spending a few minutes planning your meals and snacks for the day can prevent impulsive eating and ensure you stick to your diet plan. Prepping healthy snacks and meals in advance can save time and reduce the temptation to opt for unhealthy convenience foods.
6. Get Some Sunlight
Exposure to natural sunlight in the morning can help regulate your circadian rhythm, improving your sleep patterns and overall energy levels. Better sleep is associated with improved weight loss and maintenance, as poor sleep can lead to hormonal imbalances that affect hunger and appetite.
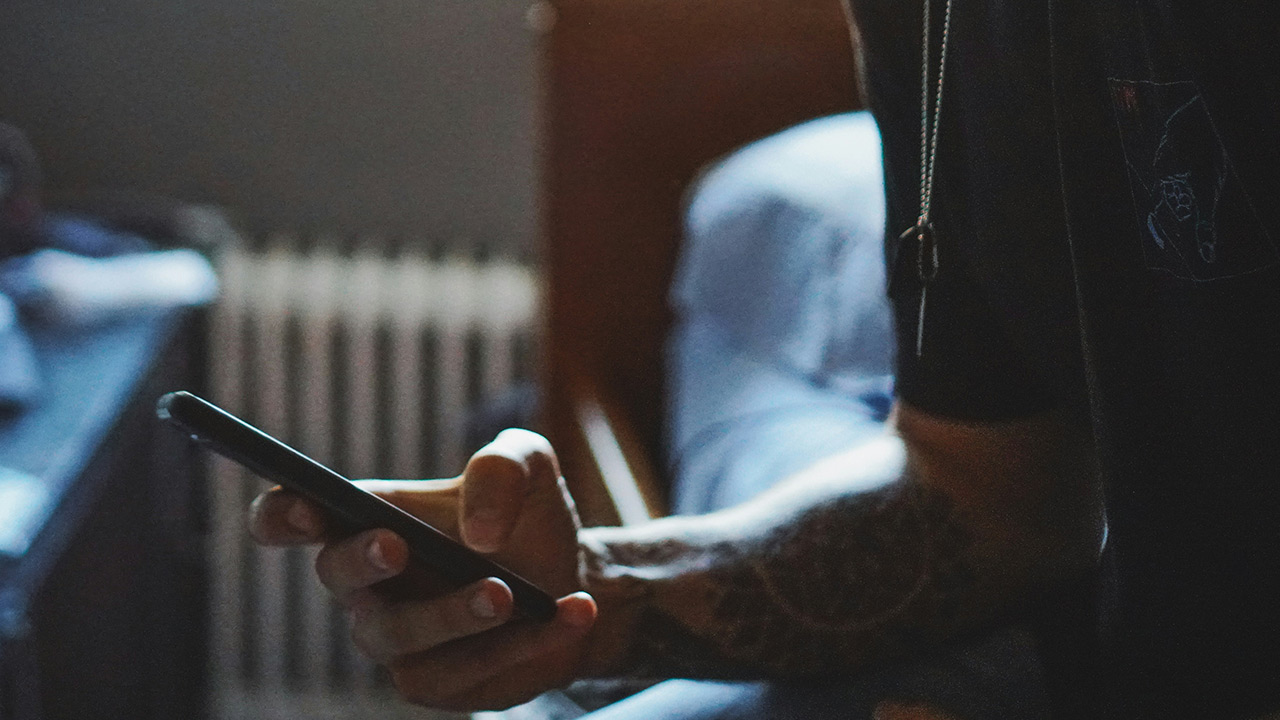
7. Avoid Checking Your Phone Immediately
Instead of reaching for your phone as soon as you wake up, take some time for yourself. Checking emails or social media can lead to stress and a rush of negative emotions, which can negatively impact your day. Spend the first moments of your morning focusing on positive, productive activities that align with your weight loss goals.
8. Stretch Your Body
Incorporating stretching into your morning routine can improve flexibility, reduce muscle tension, and enhance blood circulation. Stretching can also increase your range of motion, making your workouts more effective and reducing the risk of injury.
Conclusion
Incorporating these morning habits can create a strong foundation for your weight loss journey. By focusing on hydration, exercise, nutrition, mindfulness, and planning, you can set a positive tone for the rest of the day and stay committed to your goals. Remember, consistency is key, and small, daily changes can lead to significant long-term results. Start your day right, and watch as the benefits unfold.